How to become a Registered Nurse
This article provides in-depth information into What is a Registered Nurse? What Registered Nurses do? Degrees for Registered Nurses, Steps to become Registered Nurse and much more.
A registered nurse is a nurse who most patients deal with on a daily basis. It's your job to administer medical care, answer patient questions, and communicate any concerns to your nurse supervisor.
Becoming a registered nurse (RN) requires a nursing diploma or Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) has passed the NCLEX-RN exam administered by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) and has met all the other licensing requirements mandated by their state’s board of nursing. Registered nurses also have the potential to specialize in certain areas, such as neonatal, pediatric, geriatric, surgical, and emergency medical care. To succeed in these roles, an RN must possess strong communication skills, be detail-oriented and compassionate, and have the ability to adapt to new technologies, techniques, and medical procedures as they are introduced.
What does a Registered Nurse do ?
Registered nurses may also choose to pursue positions in teaching, management, and administration. Nurse educators, for example, are registered nurses who not only possess clinical knowledge but also teaching expertise to help train licensed practical nurses, registered nurses, and other licensed nursing staff. Additional roles in designing and implementing an academic curriculum for continuing education programs also are available for clinical nurse educators.
A registered nurse is an individual who most patients deal with on a daily basis. It's your job to administer medical care, answer patient questions, and communicate any concerns to your nurse supervisor. Specific responsibilities associated with your role can vary, depending on your speciality and work environment.
An RN, short for a registered nurse, treats patients and provides advice and emotional support to them and their families.
-
Executes orders given by physicians.
-
Administer Medication to patients.
-
Perform tests, procedures, and treatments and document them.
-
Analyse patient’s condition and report is to doctors periodically.
-
Take care of the daily needs of patients.
-
Helping other nurses to establish plans of care for patients
-
Provide primary and emergency care for injuries or illness.
- The registered nurse also leads public health education campaigns.
Steps for becoming a Registered Nurse
1
High School Diploma Or GED
Many individuals embark upon the path to become a registered nurse as early as high school. Most high schools offer students the opportunity to take college preparatory classes that ready them for the college-level coursework necessary to pursue a nursing degree. Some of the most important classes for high school students to master include math, science, social studies, foreign language, and English. Math and science classes are directly relevant to the classes that nursing students will take in their nursing degree programs. Establishing a strong knowledge base in math and science has long-lasting benefits, both academically and professionally.
2
Apply To Nurse School
After graduation from high school, the potential registered nurse must decide upon an educational path to pursue a nursing degree. Although many avenues are available to become qualified as a nurse, all nursing coursework provides training in subjects such as ethics, anatomy, microbiology, pathophysiology, fundamentals of nursing, human behaviour, microbiology, health assessment, and nutrition. Students also are expected to complete clinical rotations, during which they observe nurses as they complete their everyday duties. With a combination of clinical experience and theoretical knowledge, nurses prepare to meet the types of challenges they will encounter during the course of their careers. Although a two- or three-year associate’s degree qualifies an individual to practice as a nurse, those who study longer and seek higher degrees often earn more money and have additional opportunities for advancement.
3
Clear The NCLEX-RN Examination:
After completing a degree program, the next step is to take the NCLEX-RN exam, which is administered and scored by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing. Passing the test is a requirement for nurses in all 50 states and the U.S. military. Before nursing candidates can take the exam, they must apply for a license from their state board of nursing. Every state has different eligibility requirements for graduates seeking nursing positions, so individuals must fulfil the obligations for their state of residence preparation for the test can be quite a lengthy process. The National Council of State Boards of Nursing provides a test plan to help candidates prepare for the test. The NCLEX-RN exam is designed to gauge a nurse’s understanding of the fundamental concepts of nursing. Since it’s computerized, the test adapts to each person who takes it. As the test taker-proceeds, questions are based on answers to previous questions. The National Council of State Boards of Nursing, an organization that regulates health care standards in the nursing industry, works with state boards across the United States to establish standards within the nursing profession.
4
Pursue Professional Development Opportunities
Participating in professional development opportunities helps nurses develop their skills and grow their careers. Nurses can pursue professional development opportunities through volunteer work at a local hospital, which helps potential nurses gain experience working with patients and physicians in a professional setting. Hospitals and outpatient facilities frequently need volunteers and are happy to work with nursing students who possess some knowledge and understanding of health care. Nurses also can develop professionally by connecting with a variety of nationally recognized nursing organizations, some of which work with nurses of specific specialities. Many organizations hold conferences and events that provide learning opportunities for nurses.
5
Enter The Workforce
Once an RN passes the NCLEX-RN exam, the next step is to look for employment. Registered nurses are a vital part of the healthcare industry; therefore, they can find work in facilities all over the country, including doctors’ offices, hospitals, nursing care facilities, assisted living facilities, and home health care services. The type of facility in which an RN chooses to work has a big impact on his or her lifestyle, so this decision should be made with care. For example, registered nurses employed in hospitals and nursing care facilities often work long, unusual hours, including late nights, holidays, and weekends. However, nurses who work in doctors’ offices typically work a regular weekday schedule and are routinely off work on holidays. Some nurses change jobs as their circumstances and scheduling needs change.
6
Advance Your Career
On the off chance that an enrolled registered nurse chooses to become an advanced practice registered nurse and specialize their knowledge, a graduate degree will be required. Subsequent to finishing this education, graduates can apply for roles as certified nurse specialists, nurse anaesthetists, nurse practitioners, and nurse-midwives. The individuals who need to go further may enter a doctoral program. RNs may likewise undertake further certifications in areas such as critical care, acute care, or nursing administration.
Registered Nurse Degree Levels
Certificate
Nursing certifications are hospital-based programs providing intensive hands-on training alongside nursing coursework. Students are likewise required to take various co-essential classes in areas such as anatomy, biology, and psychology at a traditional educational institution. This experiential style of learning furnishes understudies with information of essential nursing care; they will likewise get a supplementary instruction in math and science subjects.In order to sit for the exam, you’ll need to apply for a nursing license from your state board of nursing. Since each state has different eligibility criteria, check with your state board to ensure you’ve met the requirements in order to take the exam.
Anatomy and Physiology
-
Bodily processes and parts
-
Basic understanding of human anatomy
- Vocabulary of medical terminology
Objectives
-
To understand basics of human systems
-
Identification of human body components
-
Interrelationships among systems
Psychology
-
Awareness of methodologies
-
Understanding of human psychology
-
diagnose and treat patients
Objectives
-
To understand basic principles of the human mind and behavior
-
To identify theoretical underpinnings of the major areas of psychology
-
To recognize ways of pursuing questions in Psychology
Transition into Practice
-
Refinement of nursing skills
-
Awareness of nursing trends
Objectives
-
To show nursing competencies
-
Study nursing and medical literature
-
Explore future trends in the field
Associate
An associate’s degree in nursing (ADN) includes courses in anatomy, nursing, nutrition, chemistry, microbiology among others. You’ll also be required to take general liberal arts classes. Earning an ADN is the most popular option for registered nurses and opens the door to entry-level staff nurse positions which will provide you with hands-on experience in the medical field. This is the fastest path to becoming a registered nurse as most associate’s degree programs last about two to three years. The coursework of associate degree in nursing and a nursing diploma is a lot similar, however, the coursework of associate degree is much more in-depth and it provides a more holistic educational experience.
Microbiology and Immunology
-
Microorganisms
-
Awareness of infection
-
Immunity principles
Objectives
-
Study of microorganisms and how they affect human health
-
Describe the classification, structure, and physiology of bacteria that infect humans
-
Learn about the diseases caused by anaerobic bacteria
Nursing Care
-
Experience in clinical settings
-
Ability to provide treatment
-
Obesity, heart disease, and diabetes
Objectives
-
To understand the nursing care process
-
Treat patients throughout their lives
-
Knowledge of current research to improve healthcare outcomes
Professional Issues in Nursing
-
Societal and political environment
-
Development of leadership strategies
-
Legal and ethical issues.
Objectives
-
To understand potential nursing issues
-
Legal and ethical dilemmas
-
Healthcare leadership conflicts, and healthcare policies
Bachelors
An aspiring RN can earn a bachelor’s of science in nursing (BSN) in four years at a college or university. If you’re already an RN, you can enrol in an RN-to-BSN program which is geared specifically for RNs who have an associate’s degree or nursing diploma. This path usually takes about two to three years.
An even quicker BSN option is for candidates who already hold a bachelor’s degree in another field. An accelerated BSN program allows students to apply general education credits from their first degree to the BSN. This route takes between one to one-and-a-half years.
Introduction to Nursing Research
-
Conducting medical research
-
Analysis of health research data
Objectives
-
To understand research related concepts and practice methods
-
Scientific methods and statistical analysis
-
Cultural diversity and ethical conduct of research
Chemistry and Physics for Nurse Anesthesia
-
Physical laws of fluid, matter, gas, and electricity
-
Administration of anesthesia
Objectives
-
To understand basic scientific principles for effective nurse anesthesia
-
Chemistry and physics concepts forming the basis of Anesthesiology
-
Anesthesia delivery systems and monitoring
Public Health Nursing
-
Awareness of best practices
-
Preventative care provisions
-
Population-based health issues
Objectives
-
Delivery of medical care to communities and to different populations
-
Explores rural community health nursing
-
Promote, maintain and restore health
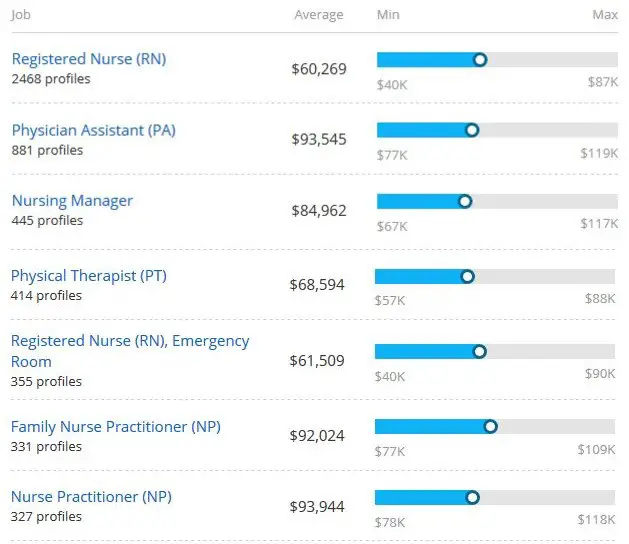
Registered Nurse Salaries
According to the US Bureau of labor statistics (BLS), the median pay for a registered nurse was $73,550 in May 2017. RNs at the lowest 10 percent of earnings had an average salary of $48,690 annually, while those at the 90th percentile earned approximately $104,100 per year. The BLS reports that those employed in the Pharmaceutical and Medicine Manufacturing industry had the highest median salary in 2017, followed by general medical and surgical hospitals, specialty hospitals, outpatient care centers, and home health care services.
An RN typically works a variety of different shifts, such as from 7:00 a.m. to 3:00 or 11:00 p.m.; from 3:00 p.m. to 11:00 p.m.; or 11:00 p.m. to 7:00 a.m. Healthcare facilities must be staffed seven days a week, 24 hours a day, including holidays. Because these shifts are harder to fill, some employers offer premium pay if the nurse is willing to work evenings, overnights, weekends, and holidays. Approximately 80 percent of RNs work full-time, while the remainder holds part-time positions.
Job growth
The BLS anticipates that the demand for registered nurses will remain steady at 15 percent annually (much faster than average) through at least 2024, a significantly higher rate than the projected 7 percent expected to increase for all occupations combined. Several factors play into the demand, including:
-
An aging population. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, one person in eight in the United States is over age 65.
-
Advances in medical technology allow people to live longer lives, which means that some people may require ongoing nursing assistance for lengthier periods.
-
More people have access to health care because of the Affordable Care Act, which made health insurance more available.
-
More people require the care of a registered nurse at home or in an outpatient facility because of the rapid discharge of patients from medical facilities.
-
The nursing shortage caused by older nurses retiring and few nurses entering the field.
Concentrations to consider for a Registered nurse
Cardiac nurse:
One of the leading causes of death in the United States today is heart disease. The demand for cardiac nurses continues to grow with the rising number of patients affected with heart-related problems. As a cardiac nurse, you will also assist with surgical procedures such as bypass, angioplasty, or pacemaker surgery.
Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA):
A Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) is a highly trained nurse that specializes in assisting with anesthesia during surgeries. CRNA’s make up some of the highest-paid nurse specialties in the medical field due to the high demand of these nurses in surgical settings and detailed training they receive. In order to become a certified registered nurse anesthetist, you must complete a degree from a graduate-level program.
Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS):
Clinical nurse specialists are a type of advanced practice registered nurse (APRN), who provides direct patient care by working with other nurses and staff to improve the quality of care a patient receives. They often serve in leadership roles and may educate and advise other nursing staff.
Stand out skills for Registered Nurse
Organizational skills: It is quite evident that every RN has to be organized and perform activities in a planned manner. Each nurse can be given many patients to look after at a time, so it is better if the nurse remains prepared for shouldering all the responsibilities. It will be beneficial while filling medical charts and allocating medications.
Stress management: A nurse has to go through continuous mental and physical trauma and stress. The workload is heavy and also hectic. RNs have to handle every kind of emotions of the patients, like anger, frustration, pain, and agony. In such situations, it is important and crucial that every nurse tries to remain calm and understand the circumstances.
Communication skills: This is the most vital quality required in an RN because he/she has to interact with patients, coworkers, and doctors. They can’t give complete care if they don’t have good communication skills. A nurse should also be a good listener, and the conversation has to be soft and polite. RNs with knowledge of multiple languages are generally paid higher.
Detailed oriented: The nurses have to be very agile, focused, and detail-oriented. They prepare patient’s reports and provide medications. There is no scope for any slightest mistake because it can critically risk the life of a patient. In this field, even a minor detail holds great importance and significance.