How to become an Electrical Engineer
This article provides in-depth information into What is an Electrical Engineer? What Electrical Engineers do? Degrees for Electrical Engineers, Steps to become Electrical Engineer and much more.
If you’re wondering how to become an electrical engineer, you're in the right place.
And, fortunately for you, the path to becoming an electrical engineer is straightforward and simple, and you can get started in an engineering program quite easily.
In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to become an electrical engineer.
What does an Electrical Engineer do ?
An electronics engineer is a professional who works on developing electrical systems and circuits to transmit power and electricity. This profession deals with designing and developing electronic devices using electricity, electromagnetism, electronics, and other related technologies.
Electrical engineers have a wide variety of responsibilities. Here are a few of the primary ones:
- Design, develop, test, and manage the manufacturing of electrical systems.
- Design ways to improve products using electrical power.
- Direct the installation, manufacturing, and testing of electrical equipment.
- Manage electrical projects to oversee the quality and timeline of the work.
An electronics engineer may work in a variety of industries, including government, aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, telecom, utilities, consumer goods, research and development, and more.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), electrical engineers are employed throughout the country, in every state in the nation.
Steps for becoming an Electrical Engineer
1
Get A Bachelor's Degree In Electrical Engineering
If you’re asking how to become an electrical engineer, the first step is to earn a Bachelor's Degree in Electrical Engineering in an engineering program that is accredited by the ABET Board for Engineering and Technology.
While there are many Electrical Engineering Bachelor’s Degree programs out there and each varies, the coursework always includes general classes with core subjects. Students in these courses will learn to deal with electrical systems, circuits, and more. Students will also gain practical knowledge and hands-on experience during labs and internship programs.
2
Consider A Master’s Degree
While a master's degree is not required to work as an electrical engineer, some students prefer to obtain a Master’s electrical engineering degree in addition to a Bachelor’s degree.
A master's degree program provides a better and more in-depth understanding of the electrical circuits, devices, and other concerns associated with the field.
A master's degree is beneficial for students who are career-oriented and want to explore more advanced career opportunities. It’s also required for anyone who wants to go on to teach electrical engineering at a University level, or who is interested in pursuing a Ph.D. in electrical engineering at a later date.
3
Pass The Fundamentals Of Engineering Exam
The Fundamental of Engineering (FE) Exam is essential for electrical engineers to become licensed. To apply for the exam, you must meet certain requirements — lead by the simple fact that you must have graduated from an Electrical Engineering Bachelor’s Degree program accredited by the ABET-Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology.
Once you’ve passed the FE exam, you’ll gain a new title — "engineer-in-training" or "intern" — which will last until you pass the Professional Engineering (PE) exam at a later date.
4
Get A Job And Gain Experience
Now that you’ve gotten all of your professional certifications and education, it’s time to get out into the field and get to work. By getting an entry-level job, electrical engineering degree graduates complete professional fieldwork. They also gain experience under the supervision of trained electrical engineers.
5
Pass The Professional Engineering (PE) Exam
The PE Exam is the last step to a career as a professional engineer. Before you can take it, though, you must have four years of experience working as an intern. Once you’ve taken and passed the exam, you’ll receive a professional engineering license in your state.
To maintain your professional engineer license, most states require you to obtain continuing education (CE) credits on an annual basis. After completing the Professional Engineering exam, you become a licensed electrical engineer.
Electrical Engineer Degree Levels
Associate
Associates Degrees are two-year programs offered at universities and community colleges. While an Associate's Degree is typically not enough education to obtain a career as an electrical engineer, it does act as a stepping stone for a Bachelor's Degree.
It also accelerates the four-year program by providing credits and experience that transfer over into the four-year program. This also offers the same job opportunity with higher earning potentials but students can be sure if they want to continue as an electrical engineer further.
Logic controllers
-
It includes digital temperature and program logic controllers.
-
Provides knowledge levels needed for PLC programming and operating.
-
Apply PLC Timers and Counters for the control of industrial processes.
Objectives
-
To provide the knowledge to understand various types of PLC registers.
-
Able to create ladder diagrams from process control descriptions.
-
To provide the knowledge about understand various types of PLC registers.
Analog electronics
-
It includes design paradigms, current mirrors, and transistor stages.
-
Examine the building blocks of analog electronics through graphical, analytical and computer tools.
-
Linear voltage regulators, differential amplifiers and active filters are some of the topics typically discussed.
Objectives
-
Gains equations for the Instrumentation Amplifier configuration.
-
Inverting and Non-Inverting configurations.
-
Infinite input impedance and voltage gain.
Computer structure and logic
-
Understanding of the use of computers in electronics,
-
Its operation, working, and the functions that can be performed using a computer.
Objectives
-
Understand computer use in electrical systems
-
Analyze the internal structure of the computer
-
Basic assembly of the computer
Introduction to Networking
-
Understanding of the data communication between the computers, softwares, hardware and resources
-
coding and decoding, electric switches and network protocols with its functions.
Objectives
-
Understand and Design network protocols
-
Understand the hardware and software components of the computer
-
The network communication technologies
Bachelors
The Bachelor’s Degree is a four-year program that provides both practical and theoretical knowledge for graduates. To get licensed as an electrical engineer, you must have at least a Bachelor’s Degree. People who want to work as Electrical Engineers can obtain a Bachelor’s Degree and search for a job. If you’ve completed an Associate Degree program, you can transfer the credits from the Associate's Degree into your Bachelor’s program, although requirements vary from school to school.
A Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering provides education in all the issues and considerations associated with electrical engineering. When you choose the right electrical engineering Bachelor’s Degree Program, you should emerge from the program feeling prepared and ready for the career ahead of you.
Electromagnetic
-
Relating to the interrelation of electric currents or fields and magnetic fields.
-
The physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles.
-
Time-varying electric and magnetic fields are coupled in an electromagnetic field.
Objectives
-
To identify, formulate and solve fields and electromagnetic waves.
-
Able to design reception of electromagnetic wave system.
-
Designs of circuits using Conductors and Dielectrics.
Circuits and digital logic
-
Makes logical decisions based on the different combination.
-
Generally only have one digital output.
-
It’s a basic building block from which all digital circuits systems are constructed from.
Objectives
-
Error Correction and Detection.
-
Digital signals can be regenerated to achieve lossless data transmission.
-
It permits data to be stored and retrieved without degradation.
Microprocessor systems
-
This course provides knowledge on the structure of the microprocessor,
-
Their working, structure, application
-
Programming of Microcontroller systems.
Objectives
-
Understand the microprocessor families
-
Control structure and building of the microprocessor systems
-
Microprocessor interaction with the external devices
-
Uses as a time or a controller to the analog interfaces
Probability theory
-
Possible calculations of data and bandwidth,
-
Managing the network traffics
-
Variables, distribution, and density functions and laws of data.
Objectives
-
Introduction to probabilities in economic theory.
-
Learn the algorithmic design
-
Calculation of probabilities to make engineering decision
Masters
If you want to take your education further or would like to obtain a more professional position, a Master’s Degree might be right for you. Once you’ve graduated with a Bachelor's Degree, you can opt to return to school and obtain a Master’s Degree, which is generally a two-year program.
Students in a Master’s Degree program will complete an in-depth thesis on a study subject of their choosing. Topics could include power systems, control systems, or telecommunication, among others.
Complex variables
-
Domain and range are subsets of the complex plane.
-
Multiple graphics will be used to provide 4-D graphical representations of analytic functions.
-
Evaluation of integrals and multivalued functions.
Objectives
-
Study of differentiable functions of one complex variable.
-
Complex representation is much "cleaner", with fewer caveats.
-
Using a mix of real and 'imaginary' numbers to explain things in the real world.
Computer engineering and architecture
-
It is a bridge between Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
-
It links hardware implementation with system and software application.
-
It includes drawing and designing and coding and logic.
Objectives
-
Uses of information technology such as analysis, simulation, design, and planning.
-
Design of hardware and software elements of computer systems.
-
Using innovative mechanisms and integrating software techniques.
Semiconductors
-
This class teaches the use of semiconductors and how it works in an electric circuit with its electrical properties.
Objectives
-
The movement of electrons and holes in the semiconductor when the electricity is passed.
-
Applications of the semiconductors in controlled electric flow
-
Learn concepts of photodetectors, laser, and quantum dot operators
Power systems
-
This course details the energy conversions from electrical to mechanical energies,
-
How electrical energy is used in the transmission of power for the industries and transportation through power cables and transformers.
-
The conversion from other sources of energy such as wind, solar, and hydroelectricity.
Objectives
-
Installation and maintenance of the power systems in industries
-
Power systems in power plants
-
Calculate the power flow through the electrical systems.
Doctorate
Students who want to pursue top-level jobs as researchers, developers, or professors at the university level can choose to pursue a doctoral degree in Electrical Engineering. A Ph.D. student utilizes the period of the degree program to conduct in-depth research and may also engage in teaching courses to the undergrad students.
A doctoral degree is significantly more complex than other degree options and will require much more research and academic investment than a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree. The degree program covers diverse concepts such as electronics, mathematics, software, technology, theoretical electricity, and other core knowledge.
A Ph.D. program in electrical engineering incorporates the nuts and bolts of electronic frameworks and plans and prepares a student for a competitive, advanced career.
A Doctor of Philosophy in Electrical Engineering degree program incorporates preparing on the nuts and bolts of electronic frameworks and plans. Some present electrical building accentuation zones incorporate semiconductors, strong state microelectronics, remote systems, and electromagnetic.
Electrical power system
-
An electrical component deployed to supply, transfer, store, and use electric power.
-
It is the grid that provides power to an extended area.
-
It includes wind solar electric, geothermal and small-scale hydroelectric generation.
Objectives
-
Helps in assessing the quality of the power.
-
Identifying issues such as voltage sags, swells, and transients.
-
Generate electricity by using heat to produce steam that turns turbines.
Integrated circuits
-
Known as chip or microchip.
-
It is a semiconductor wafer on which millions of tiny resistors and transistors are fabricated.
-
It can function as the counter, timer, or computer memory.
Objectives
-
Embedding as many transistors as possible on a single semiconductor chip.
-
It is a building blocks of most electronic devices and equipment.
- As large number of components can be packed into a single chip.
Electromagnetic and computational methods
-
Numerically study complex systems by means of a computer simulation.
-
Encourages a well-rounded understanding of the subject.
-
Makes efficient and accurate formulations for electromagnetic applications.
Objectives
-
Make specialized use of generic integral-equation and finite-element methods.
-
Error analysis and the convergence behavior of numerical results.
-
Direct and iterative algorithms for the solutions of linear systems.
Online Courses in Electrical Engineering
An online college providing electrical engineering degrees offers exposure to a wide range of topics. These programs are ideal for students who need the flexibility of an online program and do not want to attend a traditional university.
If you’re interested in pursuing an online course in electrical engineering, here are a few course elements to look for:
A Prestigious University
The best electrical engineering programs come from the best universities. As you navigate how to become an electrical engineer, look for programs offered by top universities. These programs will be well-known, accredited, and well-organized.
Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Most online courses offer a mixture of synchronous (live classes held at regular weekly intervals) and asynchronous (recorded classes available to complete at your convenience) learning. These programs are in demand for a few reasons.
First, they provide the convenience and flexibility that most people looking for an online course in electrical engineering need. Secondly, they provide a nice mixture of flexible course programming and live, in-person group work that mimics the feeling of a brick-and-mortar university.
Options for in-Person Intensives
If you love the feeling of working with other people in a group setting, consider an online course that offers an annual in-person intensive. These intensives typically take place on the campus of the University and last for a long weekend.
The purpose of the intensive is to bring all online learning students in a specific program together to meet, work on projects, and enjoy some collaborative group work. These intensives are an excellent way to get to know your program cohort and deepen your online learning experience.
Accreditation
Any online degree program you consider should be accredited. No matter what your career goals may be, accreditation status is one of the most critical considerations for any prospective student.
If you attend a university that is not accredited, it will affect your ability to obtain a professional license down the road. It may also prevent you from applying for or claiming student loans or scholarships. Additionally, a school’s accreditation status impacts the transferability of its courses, as well as a student’s future job outlook.
In the U.S., colleges and universities obtain accreditation from agencies cleared by the U.S. Department of Education. The accreditation process requires an extensive review of the school’s educational offerings and student services and verifies the quality and standardization of the university.
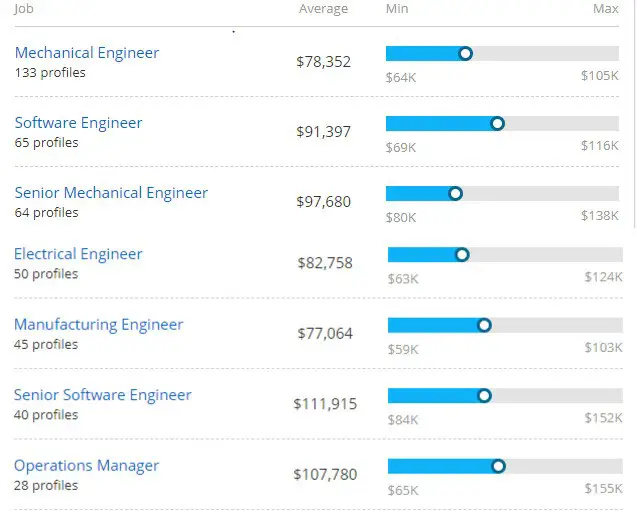
What do Electrical Engineers Earn?
Part of the reason that Electrical Engineering is so popular is that electrical engineers make a very livable wage. According to the recent statistics from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average salary of an electrical engineer is about $105,990 annually.
Job Growth
Electrical engineers are said to be competitive and are updated with the latest technologies, where they can be hired in any field due to this. According to the U.S. Department of Labour, there is an increase of 7 percent and 10,700 new jobs will be created by the end of 2022.
This means that pursuing a career in electrical engineering is a wise career decision for anyone interested in the field. Fortunately, there are many Universities that offer outstanding electrical engineering degrees, and finding the right one for you is simple.