How to become a Licensed Practical Nurse
This article provides in-depth information into What is a Licensed Practical Nurse? What Licensed Practical Nurses do? Degrees for Licensed Practical Nurses, Steps to become Licensed Practical Nurse and much more.
A Licensed Practical Nurse is a vital member of high-performance healthcare professionals providing care in a variety of settings. They typically monitor a patient’s vital statistics, administer basic care and report concerns to registered nurses and physicians. When patients enter a healthcare facility, LPNs assist the registered nurse or other healthcare providers by measuring and recording blood pressure, weight, height, pulse, temperature and rate of respiration of the patient.
What does a Licensed Practical Nurse do ?
These professionals assess patients, monitor vital signs, and assist with personal care and procedures such as catheterization and wound care.
-
Monitoring basic patient health such as vital signs and overall condition
-
Changing dressings or inserting catheters
-
Taking patient histories and maintaining documentation
-
Assisting with tests or procedures
-
Providing personal care, such as helping with bathing and toileting
-
Consulting with RNs on care plans
Steps for becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse
1
Complete An Approved Education Program
You can complete an approved program to become a licensed practical nurse in two ways, either by earning a diploma or certificate or by earning an associate degree. A diploma or certificate is often the fastest route into the workforce, but credits from these programs cannot be used toward further education. Students aspiring to become registered nurses may find an associate degree offers the best option for future career goals.
2
Qualify The NCLEX-PN
After completion of an approved Licensed Practical Nurse program students have to appear and qualify the National Council Licensure Examination for Practical Nurses (NCLEX-PN) developed and administered by National Council of State Boards of Nursing. Those who do not pass must wait 45-90 days before retaking the test.
3
Join The Workforce
After completing the program and earning a license, a student can join workforce immediately. Demand for Practical Nursing is continuously growing and the students will have plenty of opportunities to join a workplace of his/her preference.
4
Get Additional Certification
A student can choose to get an additional certificate to stand out from the crowd and increase his marketability. There are numerous certificates available for specialized clinical roles.
5
Pursue Additional Training
After being in their role for a while, LPNs may decide to engage in further education, such as a nursing degree at the associate or bachelor’s degree level. Both options generally provide wider employment opportunities and increased earning potential. Similar to the LPN career path, aspiring RNs will need to meet state requirements and pass a standardized national exam before being fully licensed.
Licensed Practical Nurse Degree Levels
Certificate
The LPN diploma and certificate are both terminal programs, meaning they are not intended to transition students to a higher level of education. Coursework covers the essentials of practical nursing, including anatomy and physiology, developmental psychology, biology, and chemistry. Students will learn about these topics both in the classroom and through clinical instruction.
Practical Nursing
-
Understanding of medical ethics
-
Development of communication skills
-
Knowledge of clinical care
Objectives
-
Focus on pathophysiology
-
Diagnostic testing
- Treatment process for disease and injuries in adults and children
Anatomy and Physiology
-
Human body’s structure and function
-
Keen knowledge of human systems
-
Ability to apply this knowledge to patients
Objectives
-
Therapies used in the treatment of mental disorders
-
Assess client for factors that affect stress level
-
Assess the client for needs related to culture
Advanced Practical Nursing
-
Advanced understanding of clinical care
-
Development of physical stamina
-
Learning how to offer empathetic care
Objectives
-
Instruction in how to care for patients
-
Receiving treatment via intravenous methods
-
Arterial puncture and blood withdrawal equipment
Associate
Associate’s Degrees are offered at community colleges and often provide graduates greater career flexibility. An associate degree can be used as the foundation for a bachelor’s degree, whereas credits earned in a diploma or certificate program typically cannot be transferred to an advanced degree. In addition to covering all foundational nursing coursework, associate degrees include a more in-depth study of relevant topics and offer additional classes as electives.
Medical/Surgical Nursing
-
Understanding of anatomy and physiology
-
Critical thinking and problem-solving
-
Hands-on clinical experience
Objectives
-
Concepts of practical nursing and clinical care
-
Use therapeutic nursing
-
Demonstrate safety and effectiveness in performance
Mental Health Concepts
-
Signs of common mental disorders
-
Legal and ethical guidelines
-
Prioritize patient needs
Objectives
-
Use anatomical terminology
-
Identify causes and effects of homeostatic imbalances
-
Apply appropriate safety and ethical standards
Intravenous Therapy
-
Mastery of administration of IV medication
-
Ability to withdrawal blood
-
Development of empathy for patients
Objectives
-
Instruction in clinical skills
-
Integrate theoretical and scientific concepts
-
Engage in lifelong learning
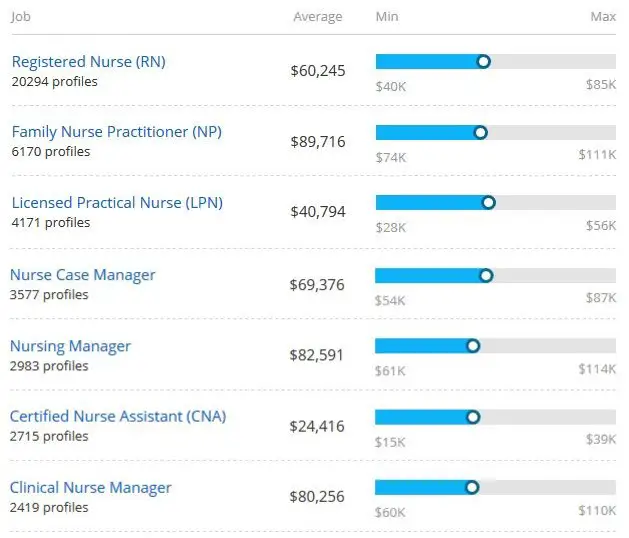
Salary of a Licensed Practical Nurse
The average annual salary of an LPN is $46,200 approximately, as per the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The bottom 10% of LPN earn about $33,000 per year and the top 10% earn $61,000 approximately per year.
Job Growth of a Licensed Practical Nurse
As per the BLS, the employment rate of LPNs is projected to grow at 11% between 2018 and 2028. The overall need for healthcare is expected to increase because of the increase in the ageing of the baby-boom population. The demand for LPNs will increase as there will be a need for them in residential care facilities and in-home health environments to care for older patients.
Concentration to consider for Licensed Practical Nurse
The list of concentrations for an LPN to specialize in is vast. Following are some of the most popular concentrations to consider for a Licensed Practical Nurse:
IV Therapy Certification:
Iv or intravenous therapy refers to therapy that delivers fluid into the veins in the body. IV therapy is the fastest way to deliver medications, blood products and more into the bloodstream to help with various health conditions, dehydration and blood transfusions. A IV therapist's primary job is to administer medications and products via IV to patients. During the IV process, the therapist monitors the patient for any reactions and ensures that the IC stays in place. The IV therapist documents the entire IV process as well as patient updates and progress. IV therapists have a wide range of facilities to choose from when it comes to their place of work. This includes ERs, oncology units, doctor’s offices, specialty clinics among others.
Long Term Care:
LPNs -Long Term Care is responsible for administering care in a Long Term Environment. They provide basic care including administering medications, collecting specimens, bathing, feeding and dressing. They also have to document every service that they provide to their patients in every shift. They also advocate the medical needs of their patients to their physicians.
Wound Care Certification (WCC):
Wound Care Nurses is responsible for assessing, treating and creating care plans for patients with complex wounds, ostomies and continence conditions. They also educate and provide care instructions to patients and families. LPNs with at least a high school diploma and a minimum of three years of clinical experience are eligible to take the national WCC examination. WCC allows LPNs to clean and treat all types of wounds. This is one of the most popular and sought after certifications in hospitals and long term care facilities.
Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS):
LPNs specialized in PALS work in pediatric care. It is a specialty certification that trains LPNs in life-saving care for infants and children. LPNs learn how to properly assess patients, provide advanced interventions, and utilize scenarios while applying critical thinking skills.
Advanced Cardiac Life Support(ACLS):
ACLS is an advanced certification program. LPNs who are certified in ACLS are trained to take care of critically-ill adults suffering from cardiovascular problems. ACLS LPNs usually work in ERs and ICU units of a hospital or a specialty clinic.
Basic Life Support (BLS):
LPNS specialized in BLS are trained to promptly recognize several life-threatening emergencies, give high-quality chest compressions, deliver appropriate ventilations, and provide early use of an AED.
Stand Out Skills for an LPN
Following are skills required for becoming successful as an LPN:
Clinical Skills: LPNs perform a wide range of duties in their day to day lives. Clinical skills include identifying a patient’s problems based on indicators like skin color, pulse, blood pressure amongst others. Clinical skills prepare LPNS to actively and effectively participate in the delivery of caring for patients and their families. Clinical skills are of utmost importance for an LPN
Communication Skills: LPN needs to communicate with their patients, families, and doctors. Effective communication is very important for the fast execution of work. LPNs should be able to understand the details of the patient and be able to deliver the right information to the RNs who make the health care plan for the patients.
Decision-Making skills: one of the most important skills for an LPN to have the ability to make quick and right decisions. During emergencies, an LPN should be able to make the right and correct decisions so as to be able to perform the necessary procedures quickly and effectively
Detail Oriented: LPNs must be agile, focused and detail-oriented. LPNs are responsible for diagnosing and providing medications during the treatment process. They should make note of every minute detail. A single small error can have serious consequences in the health condition of the patient. Hence, it is important that nurses are accurate and have a knack for details.