How to become an Economist
This article provides in-depth information into What is an Economist? What Economists do? Degrees for Economists, Steps to become an Economist and much more
Economists play the role of a practitioner of socialism whose concerned concepts are goods, services, forecast market trends in the future, economy, and draw conclusions based on the insights they get from the research. They even provide advice and suggestions on stock markets, the latest trends through their analysis and understanding of economics. Being an economist is not easy and is considered to be one of the stressful jobs.
If you are willing to become an economist here is what you should do,
- Gain a bachelor's degree
- Pursue a Master's degree
- Complete an internship to gain experience
- Consider Ph.D. (Optional)
- Gain Certifications
The career of an economist can be understood by these details tabulated,
|
Career Title |
Economist |
|
Degree Requirements |
Master’s degree (in Finance or Accounts) |
|
Job Growth |
8% |
|
Experience required |
1-2 years |
|
Salary (2020) |
$89,764 |
|
How long to become an Economist |
6 years |
|
Required Skills |
Communication, problem-solving, technically sound, analytical skills. |
What does an Economist do ?
An economist can be defined as an individual who practices the monitoring of the distribution of goods and services, countries present trends, and use tools to come to conclusions and provide a solution.
They work on the distribution of available resources equally. These resources include machines, operating materials, services, goods, labor, and more. They also monitor current economic trends, analyze and conduct research on the data that has been collected.
Duties of an Economist:
-
Conducting research on the current market.
-
Formulating methods to collect data.
-
Providing economic advice to stakeholders.
-
Evaluating past and present economic trends and issues.
-
Writing technical and non-technical papers on economic trends and forecasts.
-
Assessing the impact of different events on the economy of stakeholder.
-
Analyzing the efficiency and performance of a company.
-
Preparing briefs for government ministers and answering their queries.
Steps for becoming an Economist
1
Start While You're Still In High School
To be an expert in economics you have to start preparing yourself at an early level. Take maths, economics and statistics classes in high school. It will make your college much easier as the major subjects are totally based on Maths and Statistics. You will have to be really good with numbers to greatly succeed in this field. You will get fundamental knowledge about economics. You should also start reading the newspaper and watching the news on the latest economic reforms and events.

2
Get A Bachelor’s Degree
A minimum of a bachelor's degree is a must for any job and hence you should definitely have it in the first. To be an economist you should major in economics, business management or maths-related field like statistics.
You will basically have classes in microeconomics, macroeconomics, econometrics, and economic theories. In addition to that, you may have to take classes like finance, accounting, and marketing. Have the perfect structured education would help you fetch a job that you're dreaming.

3
Get A Master’s Degree
A master's degree would surely be a great addition to your existing records. It provides you with the actual experience and gives exposure to all the aspects of economics. A master’s degree in economics can be completed in two years.
An undergraduate degree in economics or related field is not mandatory to pursue a master's in economics but students who have majored in an unrelated field may have to take additional courses.

4
Get An Internship
An internship is definitely important as it provides the actual experience to students that how the work is going to be after their education. Master's candidates often get internships during their time at college, working with a professor or private company assisting with research. This looks great on a resume and can be your foothold in the academic or professional world of economics.

5
Get A Doctorate Degree
A Doctor of philosophy in economics requires several years of study and is a research-based degree that covers advanced topics in microeconomics, macroeconomics, econometrics, and quantitative analysis.

6
Start Your Career
The private sector, particularly consulting firms and scientific and technical companies, may offer the best chances for employment for economists. Research and educational institutions will also provide employment opportunities. These will be most plentiful for applicants with masters or doctoral degrees.

7
Join The Professional Organization
Professional organizations provide members with an opportunity to network with fellow economists working in the same subfields and to keep current on advancements and research. Organizations include the Association for Social Economics and the National Association for Business Economists.

Economist Degree Levels
Associate
Job opportunities for students with associates in economics are very few. It takes about 2 years to complete this degree and offers up to 60 credits to complete the course. Students can also transfer credits easily and complete the course sooner. There are some entry-level jobs in banking, sales, accounting etc. This degree is ideal for students who already have a job and want to advance their career. Most of associate’s degrees in economics are provided online.
Microeconomics
-
Supply and demand
-
Consumer behavior
-
Economic Principle
Objectives
-
Implications of individual human action
-
Utilization and distribution of scarce resources.
-
Variety of economic environments.
Macroeconomics
-
Aggregate Supply and Demand
-
GDP, GNP
-
Money and Monetary Policy
Objectives
-
Sustainable rate of economic growth
- Balance of payments in equilibrium
-
Price stability
Global Economics
-
Globalization of Culture and Economy
-
Population Change and Structure
-
International Money and capital markets
Objectives
-
Understand economic activity of a country
-
An equitable (fair) distribution of income
-
A sound structure to public finances
Bachelors
Candidates with a bachelor’s degree qualify for some entry-level economist positions, including jobs with the federal government. Most who complete a bachelor’s degree in economics find jobs outside the economics profession as research assistants, financial analysts, market analysts, and similar positions in business and finance.
Business Economics
-
Decision making within organizations
-
Enterprise and its economic environment
-
Organisations and markets.
Objectives
-
company and its key functional areas
-
Analysis of all business functions
-
Efficient functioning of business
Econometrics
-
Classical Statistics & Simple Regression
-
Binary Response
-
Treatment Effects
Objectives
-
Statistical analysis of economic data
-
Empirical quantitative analysis
-
Estimate parameters in regressions equations
Business Law
-
Alternative legal system
-
Capital markets law
-
Elements of taxation
Objectives
-
Understanding the Legal Environment of Business
-
Law and their economic implications
-
contract law in economic relations
Masters
A master’s degree program in economics prepares graduates for further study at the doctoral degree level. Some programs allow students to choose an area of emphases, such as international economics or economic development. Others may cover wide-ranging topics in contemporary economic issues. A thesis may also be required, though some programs offer a non-thesis option.
Advanced Microeconomics
-
Preferences and Utility
-
Walrasian Demand & Hicksian Demand
-
Utility for Money
Objectives
-
Following a proof-based approach
- Firm grounding in classical microeconomic
-
Behavior under uncertainty
Financial Economics
-
Time value of money
-
Risk and Return
-
The Efficient Market Hypothesis
Objectives
-
To understand investment tools
-
Financial risks in investment
-
Asymmetric information
International Economics
-
Theory of international trade
-
Income distribution
-
International commercial policy
Objectives
-
Analysis of international trade
-
Economic development models
-
Analyze and test international trade models
Doctorate
With more education come more job opportunities (and higher pay). If you get your Ph.D., you could teach or work just about anywhere. This takes several years and includes completing detailed research in a specialty field. It is a research-based degree that focuses on the upper-level understanding of quantitative analysis.
Industrial organization
-
Mergers and Acquisition
-
Price discrimination
-
Sub-optimal consumer behavior
Objectives
-
Strategic behavior of firms
-
Regulatory policy and antitrust policy
-
Market competition.
Income distribution
-
Inequality and Mobility
-
Capital Accumulation and Income Inequality
-
Policy and Political Economy
Objectives
-
Understanding of the ideal distribution of income
-
Consumption and wealth
-
Develop methods of measuring inequality
International economics
-
Factor Price Equalization and Trade
-
Standard Trade Models and Country Welfare
-
Market Imperfections and Trade
Objectives
-
Compare alternative theories of international trade
-
Analyze and test international trade models
-
Read and analyze the nation’s balance of payment
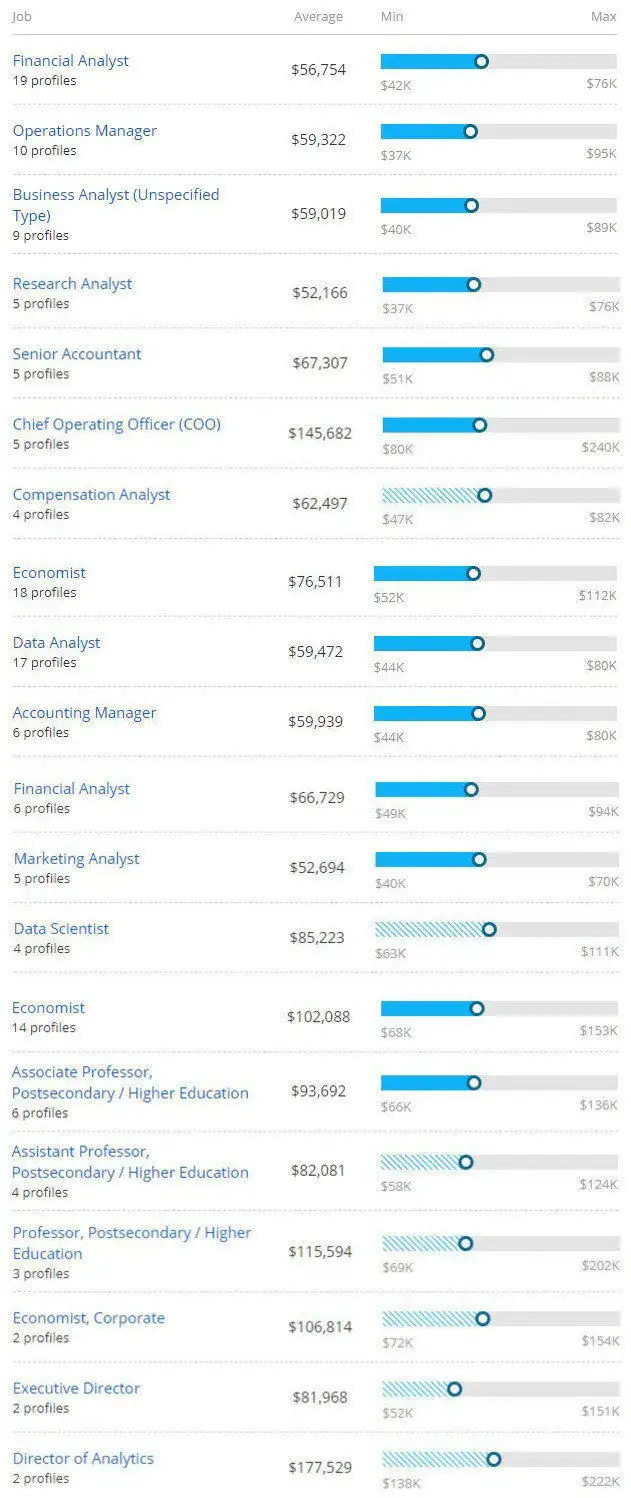
Economist’s salary
According to the Bureau of Labour Statistics, the average salary offered to an economist is about $89,265 and earnings may vary between $75,283 and $104,967. The salaries usually depend on the education, qualification, stand out skills required for the job. The top 10 percentile of economists makes $105,020 per year.
Job growth
In the United States, the job growth of an economist is predicted to be about 8 percent during the period of 2018 to 2028. Candidates who earn a master’s degree or a Ph.D. have diverse chances of career advancement. The rapid growth of job opportunities is due to the involvement of economist’s positions in every other field such as banking, health, government sectors, accounts, finance, and others.
Career Concentrations for an Economist
At times where you are aiming at becoming an economist but couldn't manage to land on that job, you can explore various other career opportunities which with similar qualification, they are,
Actuary:
Salary: $70,751
An actuary is a business professional who deals with the analysis of risk and financial uncertainties, measures the risks. They are indulged in developing business and policies to minimize the risks by combining mathematics, statistics, and financial theory to manage the potential uncertainties.
Budget Analyst:
Salary: $57,903
A budget analyst is a professional who is focused on organizing and allocating the resources in the business by developing and preparing the budget. They closely monitor the expenditures incurred within the budget and also predict the future cost requirement. Their roles include reporting and managing spendings.
Financial Analyst:
Salary: $53,250
Financial analysts are concerned with financial analysis as a role in establishing security analysis, researching an investment, and rating evaluation. They guide and suggest organization with financial decisions while they assess the stocks, bonds, and other investments.
Market Research Analyst:
Salary: $59,212
A market analyst is responsible for the data analysis of the changing market demands, supply, consumers, and competitors. Also determining the sales and service regarding a particular product and the value the customers are willing to pay.
Skills Required for an Economist
The economist is not just about working on one specific topic. An individual has to be active, read, and should be good enough to draw conclusions from them. So, to become a good economist you must adopt these skills to stand out of the crowd, they are,
Communication Skills - The first and foremost important skill that every person in any field should have is that they should be able to effectively communicate with anyone to have healthy operations and work processes.
Mathematical Skills - Economists are very close to numbers as they always involve analyzing the numerical sets, interpreting data, visualizing the future, and more. So, it is very important to have the skills of a number and should be very comfortable in handling large sets of numerical values.
Self Motivated and Being Independent - It is very important to everyone, not just economists. It is very necessary that they motivate themselves and as it is not a work that a whole bunch of team works towards one goal. It is just one person and has to be independent.
Flexibility - It is obvious here being an economist you have to be very flexible and comfortable with uncertainties. These are a few important things that need to be possessed. While there are many other skills that an economist should have, such as time management, problem-solving ability, and more.